Description
AA sequence: ACLGQWDSCDPKASKCCPNYACEWKYPWCRYKLF
Disulfide bonds: Cys1-Cys4, Cys2-Cys5, Cys3-Cys6
Length (aa): 34
Formula: C183H254N46O48S6
Molecular Weight: 4058.73 g/mol
CAS number:
Source: Synthetic
Purity rate: > 95 %
138 € – 2090 €
Phlotoxin-1 is a new member of the NaSpTx-1 family. Phlotoxin-1 has been purified originally from the venom of Phlogiellus sp., Theraphosidae Selenocosmiinae (endemic to Papua New Guinea). Phlotoxin-1 inhibits Nav1.7 with an IC50 value of 39 ± 2 nM.
Biossay results
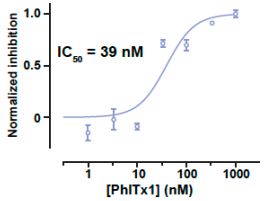
Photoxin-1 inhibition of Nav1.7 channels expressed in a mammalian cell line. Average dose-response curve of hNav1.7 current block by Photoxin-1. A sigmoid Hill fit provides an IC50 value of 39 ± 2 nM and a Hill value of 1.53. Numbers of cells per concentration: 4 to 8.
AA sequence: ACLGQWDSCDPKASKCCPNYACEWKYPWCRYKLF
Disulfide bonds: Cys1-Cys4, Cys2-Cys5, Cys3-Cys6
Length (aa): 34
Formula: C183H254N46O48S6
Molecular Weight: 4058.73 g/mol
CAS number:
Source: Synthetic
Purity rate: > 95 %
Chemical Synthesis, Proper Folding, Nav Channel Selectivity Profile and Analgesic Properties of the Spider Peptide Phlotoxin 1
Nicolas S., et al. (2019) Toxins, doi:10.3390/toxins11060367. PMID: 31234412
Phlotoxin-1 (PhlTx1) is a peptide previously identified in tarantula venom (Phlogius species) that belongs to the inhibitory cysteine-knot (ICK) toxin family. Like many ICK-based spider toxins, the synthesis of PhlTx1 appears particularly challenging, mostly for obtaining appropriate folding and concomitant suitable disulfide bridge formation. Herein, we describe a procedure for the chemical synthesis and the directed sequential disulfide bridge formation of PhlTx1 that allows for a straightforward production of this challenging peptide. We also performed extensive functional testing of PhlTx1 on 31 ion channel types and identified the voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channel Nav1.7 as the main target of this toxin. Moreover, we compared PhlTx1 activity to 10 other spider toxin activities on an automated patch-clamp system with Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells expressing human Nav1.7. Performing these analyses in reproducible conditions allowed for classification according to the potency of the best natural Nav1.7 peptide blockers. Finally, subsequent in vivo testing revealed that intrathecal injection of PhlTx1 reduces the response of mice to formalin in both the acute pain and inflammation phase without signs of neurotoxicity. PhlTx1 is thus an interesting toxin to investigate Nav1.7 involvement in cellular excitability and pain.
We use cookies to optimize our website and our service.